Various themes for your personal website based on WordPress templates can be found on the internet by searching for “website templates”. There are many, and you can always choose the parameters, design, and functionality that are required for a specific topic. At the same time, each theme can be customized if necessary. To do this, just go to the admin panel, where you can change the font, site title, description, background, and other parameters.
Sometimes, it’s necessary to change some important details, but there are no suitable tools in the panel for this. With enough determination, you can deal with this by digging into the “engine”. It contains a huge number of files responsible for different parameters and effects for all parts of the web resource. To explore important aspects displayed on the user’s screen, you can use a special guide to website design — CSS and markup — HTML.
Even with minimal design knowledge, using the guide, you can customize the required template to fit your needs. After all, that’s what a template is for — to provide a unique individuality to the site’s appearance based on a standard.
WordPress File Structure
- index.php — the main file of the WordPress theme. It defines the main layout of the site elements. This file is responsible for displaying the homepage of your site.
- header.php — the top of your site, the header.
- footer.php — the footer, the bottom part of the site, also called the “basement”.
- page.php — this file handles the display of standard WP pages.
- single.php — this file outputs the post page.
- sidebar.php — the sidebar of the site, which can be the left or right column.
- comments.php — in this file, you can edit the comment template.
- archive.php — the article archive.
- functions.php — an important WordPress file that handles its functions (registering menus and sidebars). It allows you to hide elements and add new functionality to your theme.
- category.php — in the admin panel, this is called “categories”, and it handles the display of categories and their short entries.
- author.php — you can use this file to display articles by a specific author.
- style.css — the main CSS file of your template. Here you create the visual appearance of WordPress. Remember, the commented lines at the top of the file are very important, without them your template will not work. You can rename the theme and change the description (after renaming the folder with your template).
- searchform.php — the search form template.
- 404.php — if a user enters a non-existent address in the browser, they will see this page informing them that the page does not exist. You can read more about this in our article — How to edit the 404 page in WordPress.
- tag.php — if you use tags on your site, this file will display them.
- search.php — the search query results page.
- attachment.php — handles the display of attached files.
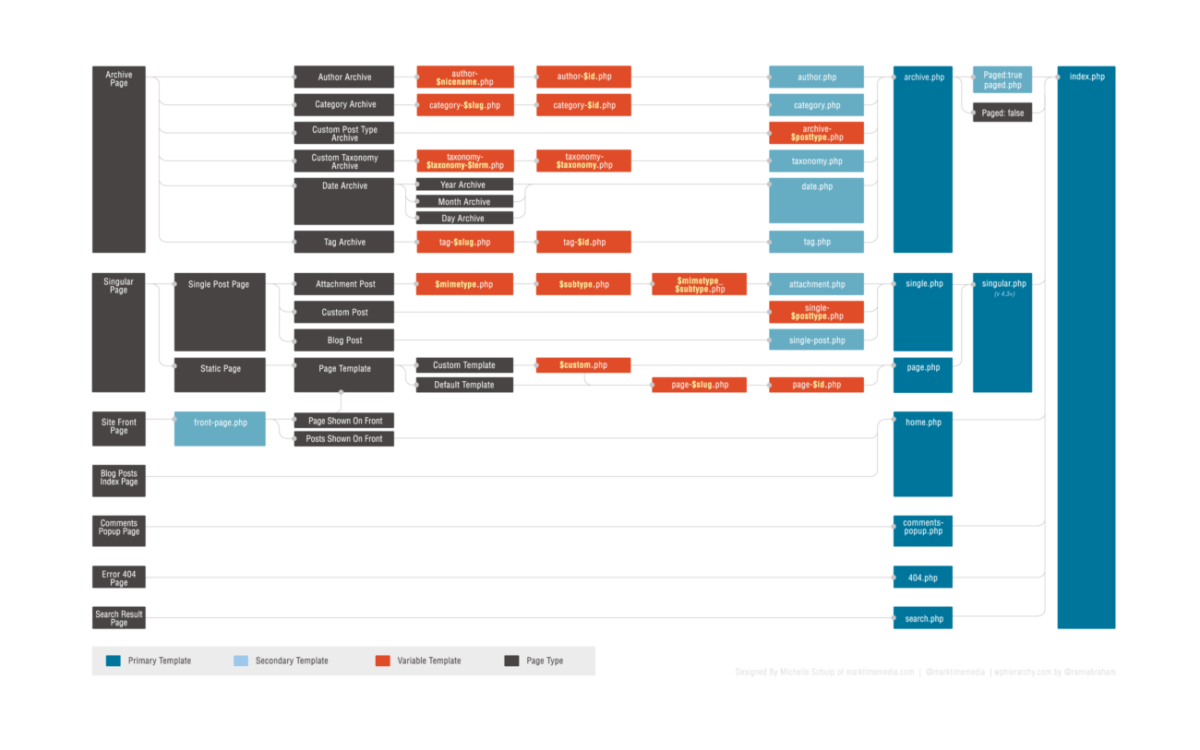
WordPress Template Structure Visually

For advanced users, we provide the WordPress hierarchy
We also recommend visiting the site https://wphierarchy.com/, where you can see a more detailed relationship between the files.
We hope that our article “WordPress File Structure (themes, templates, folders)” will be useful for you. Thank you for your attention.



Leave a Reply